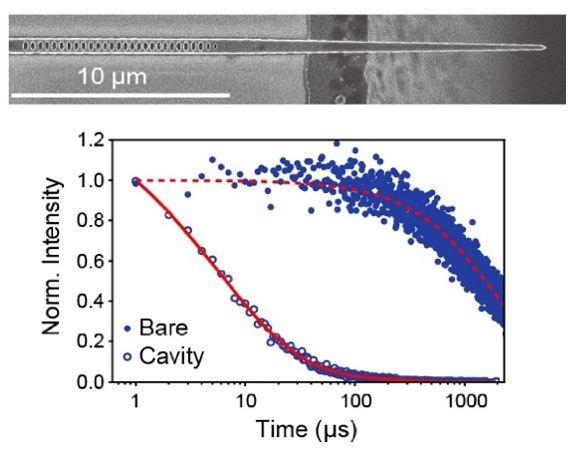
Scalable Quantum Memory Development
Demonstrating optical and spin coherence properties of epitaxial Er :CeO2 /Si at 4 K
Purcell enhancement of Er: TiO2/Si devices via atomic layer deposition
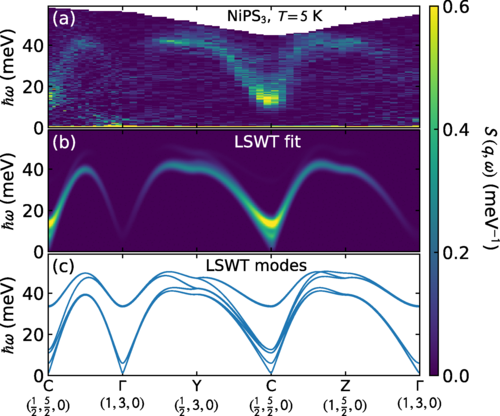
Validating Electronic Structure Models Using Neutron Scattering
Showing that electronic structure calculations provide an accurate model of a 2D magnetic material.
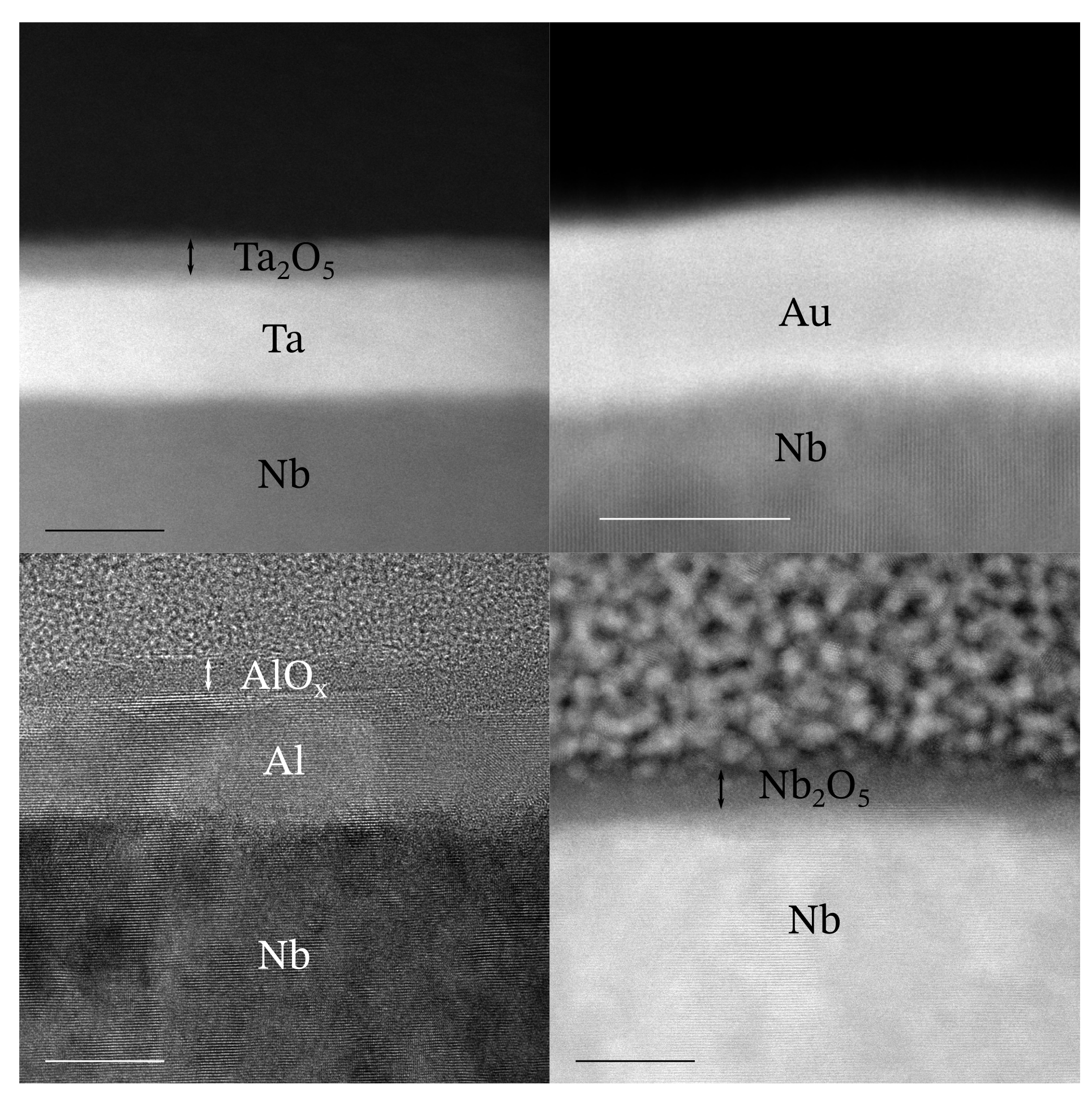
Saving Qubits from Lossy Oxides
SQMS scientists develop unique qubit fabrication techniques that enable systematic improvements in the performance of superconducting devices for quantum computing, communication, and sensing.
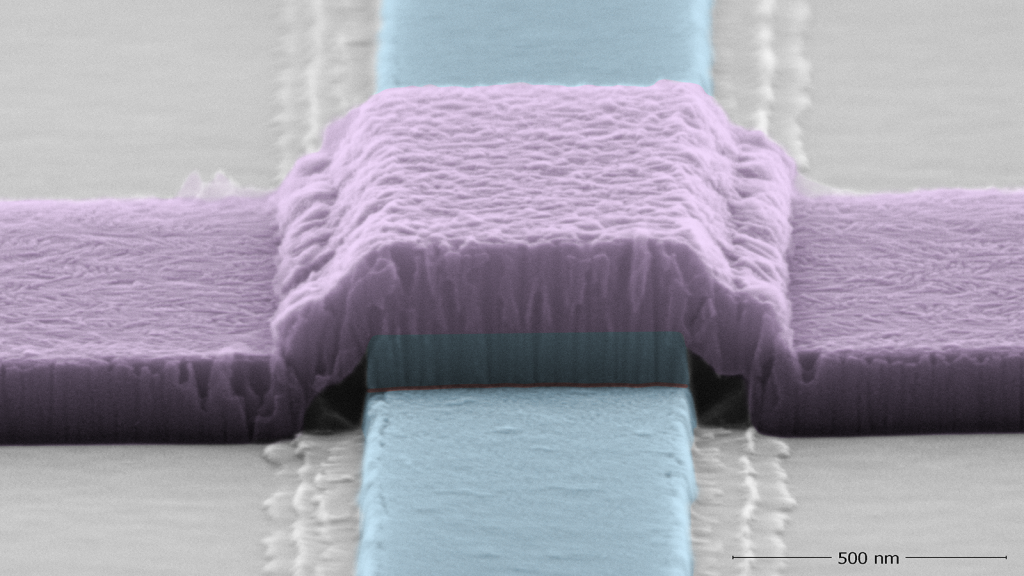
Improved Coherence in Optically Defined Niobium Tri-Layer Junction Qubits
Developed method for nanofabrication of high-coherence Nb-trilayer Josephson junctions.
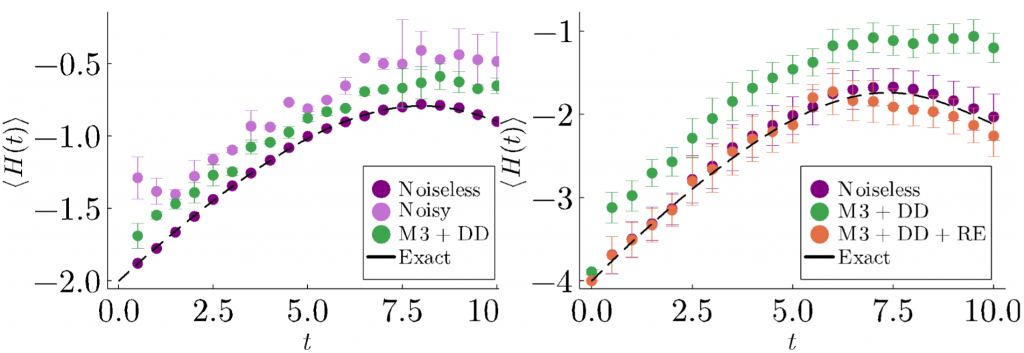
New Algorithm to Simulate Open Quantum Systems
QSA scientists designed and demonstrated a novel NISQ-friendly algorithm for simulating real-world open quantum systems on quantum computers.
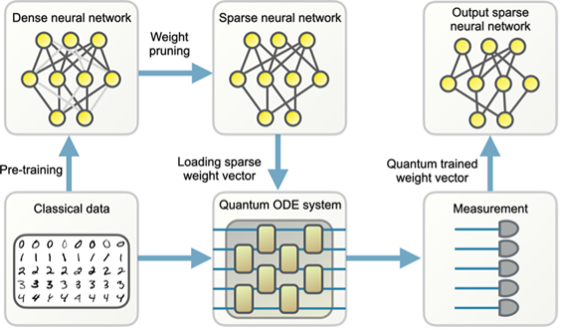
Towards Provably Efficient Quantum Algorithms for Large-Scale Machine Learning Models
Efficient quantum algorithms for large-scale machine-learning models.
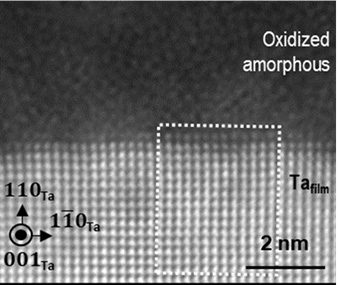
Researchers Build an Atomic-Level Model of Oxidation on the Surface of Tantalum Film
Advanced electron microscopy and first-principles calculations reveal atomic motifs at the oxidized surface of superconducting tantalum film.
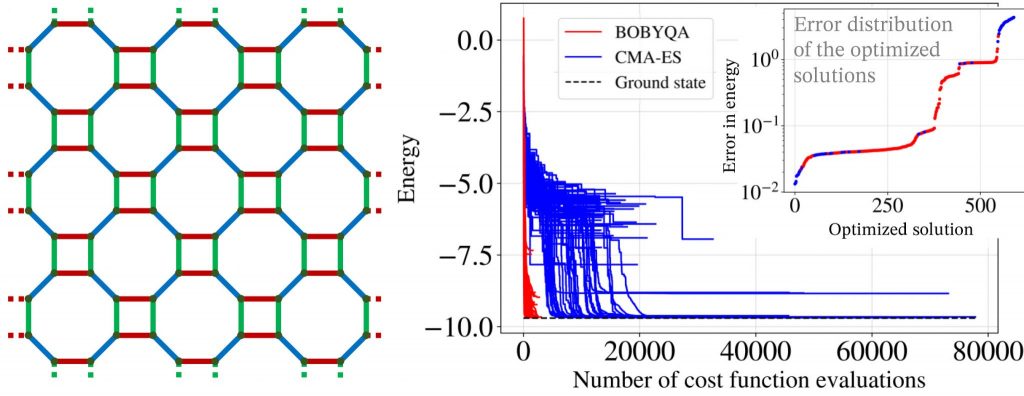
Benchmarking Variational Quantum Eigensolvers for the Kitaev Model
Advancing variational quantum algorithms on NISQ devices.
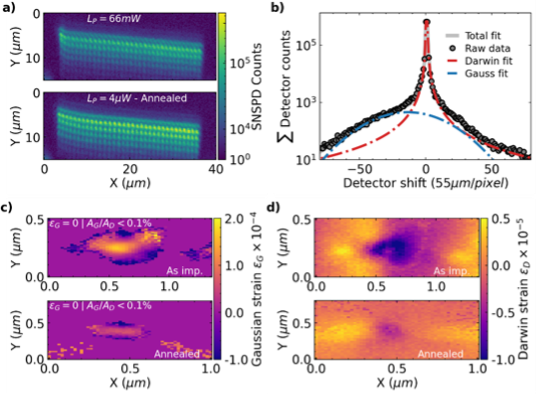
Deterministic Nanoscale Quantum Spin-Defect Implantation and Diffraction Strain Imaging
Studying the formation dynamics of divacancy spin qubits in 4H-SiC using high-resolution synthesis and strain imaging.
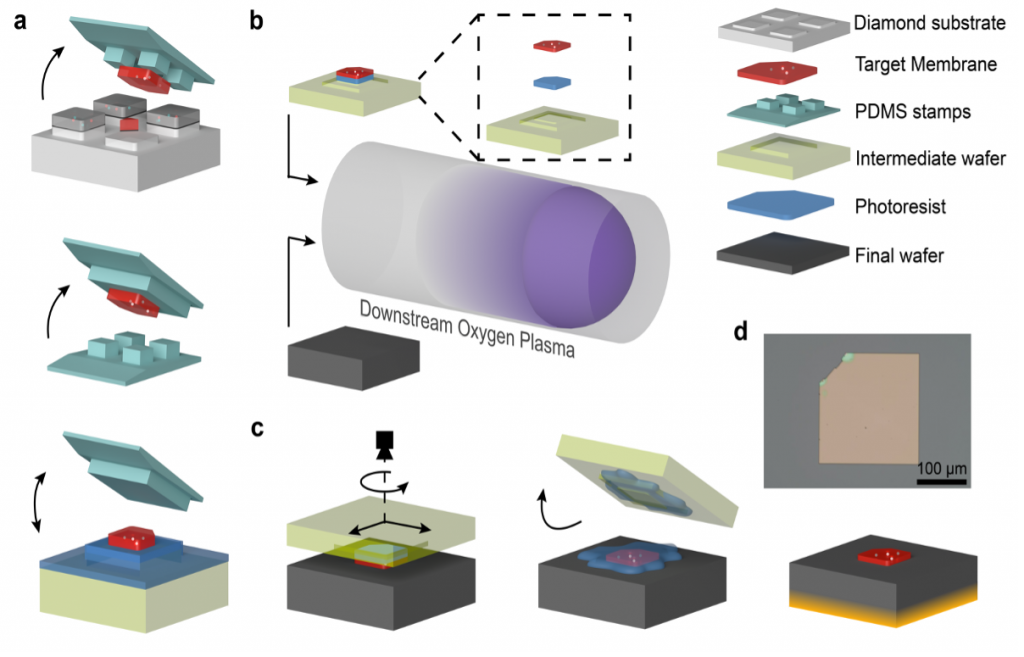
Direct-bonded Diamond Membranes for Heterogeneous Quantum and Electronic Technologies
Developing a method for direct bonding single-crystal diamond membranes to a wide variety of materials.
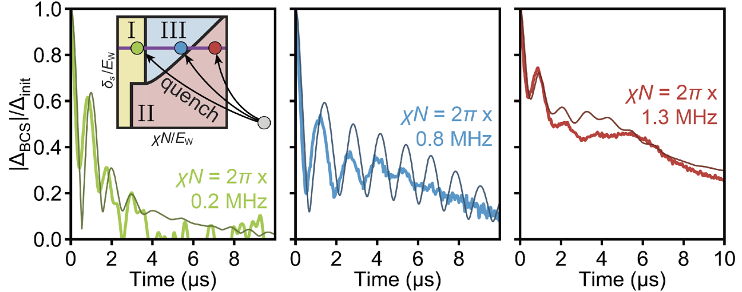
Understanding Superconductivity with Quantum Simulators
QSA scientists developed a unique programmable quantum simulator capable of predicting the out-of-equilibrium dynamics of superconductors.
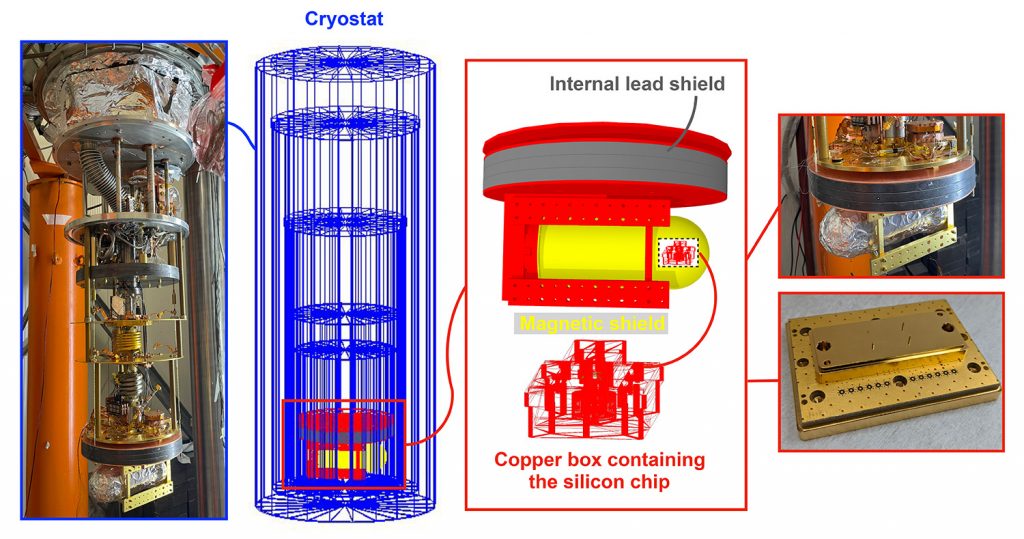
Disentangling the Sources of Ionizing Radiation in a Typical Qubit Chip
Identifying the sources of radioactivity enables the development of appropriate strategies for mitigation.
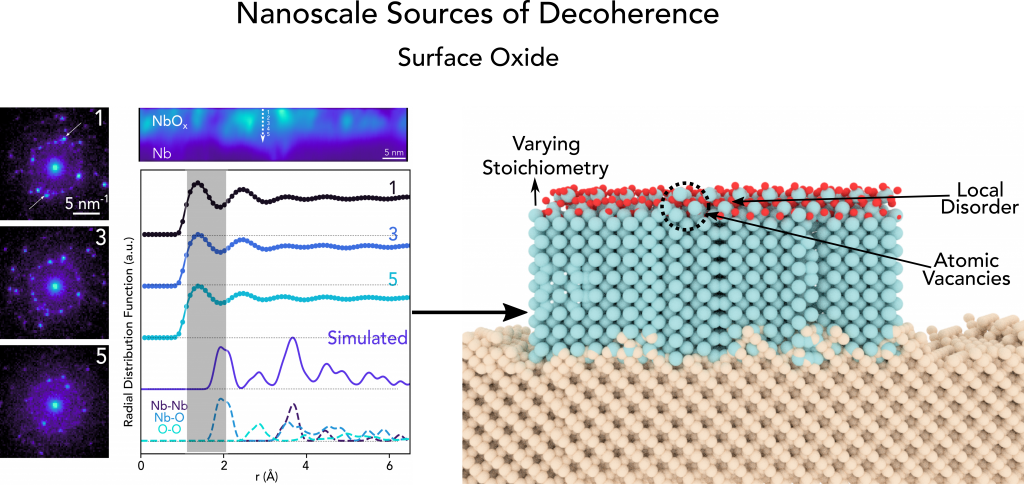
Identifying Potential Nanoscale Sources of Decoherence in Nb Superconducting Qubits
Insights regarding defects in the surface oxide help inform new methods for improving qubit coherence.
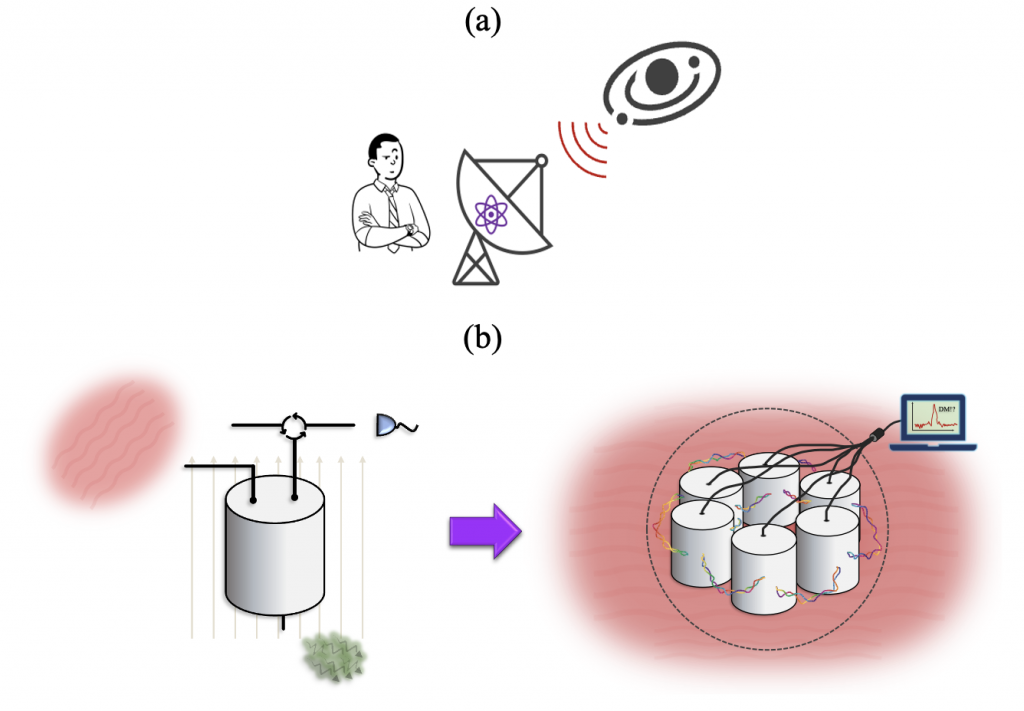
On the Hunt for Dark Matter, with Entangled Haloscopes
Exploring the role of entanglement for next-generation detector technology, with applications to fundamental physics.
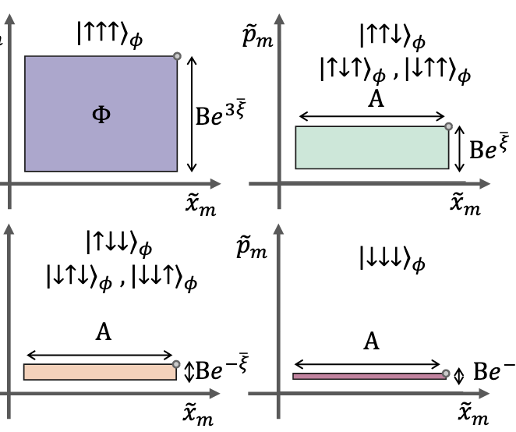
Increasing Algorithmic Efficiency with N-body Interactions foor Trapped-Ion Qubits
QSA scientists developed a novel protocol for the single-step generation of N-body entangling interactions between trapped ion qubits. This capability supports more efficient execution of quantum algorithms, which have better performance in the face of decoherence and other errors.
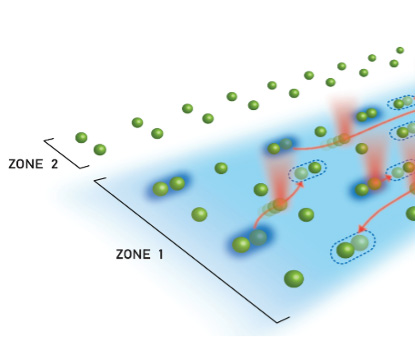
A Quantum Processor Based on Coherent Transport of Entangled Atom Arrays
Demonstrating the ability to shuttle ancilla arrays consisting of neutral atoms in optical tweezers, to realize a toric code state on a torus with 24 qubits. These results pave the way toward scalable quantum processing and enable new applications from simulation to metrology.
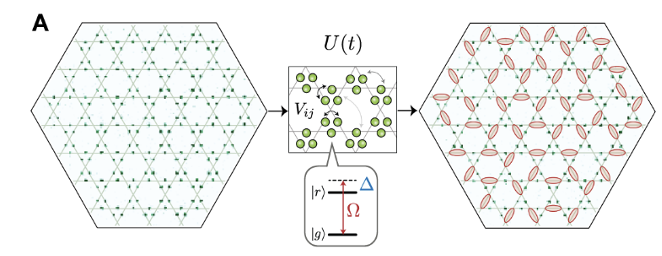
Encoding Topological States in a Neutral Atom Simulator
QSA scientists used a neutral atom quantum simulator to observe the onset of a quantum spin liquid phase, demonstrating how these flexible systems can be used to experimentally explore topological materials that have been a major focus in physics for the past several decades.

Scalable Simulation of Quantum Circuits
Navigating noise on GPU-based HPC systems